A met also is defined as oxygen uptake in ml/kg/min with one met equal to the oxygen cost of sitting quietly, equivalent to 3.5 ml/kg/min. Here's how to use them. We will share several comprehensive met charts below as well. Web a met, or metabolic equivalent, is described as the amount of energy it costs to complete a task, determined by the amount of oxygen it requires. Access our metabolic equivalent chart, a valuable tool for customizing exercise plans based on patients' fitness levels and health goals.
Web for each person, the range for total daily energy expenditure is highly variable, it depends on many factors, including: Web this met activity chart is designed to help individuals and healthcare professionals estimate the energy expenditure of various physical activities. A met also is defined as oxygen uptake in ml/kg/min with one met equal to the oxygen cost of sitting quietly, equivalent to 3.5 ml/kg/min. Web met levels go over 10, but much of what you need to know for acute and inpatient rehab, e.g., for adls and iadls are covered up to 4.1 mets. Web met chart approximate energy cost of activities — 1 met is the energy expenditure at rest note:
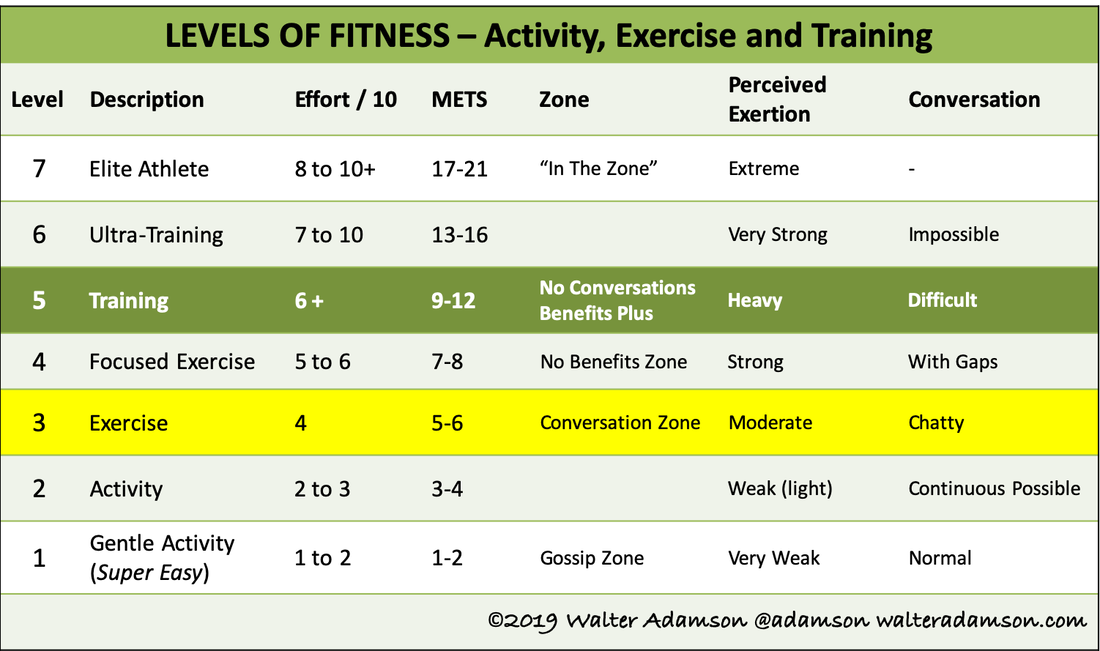
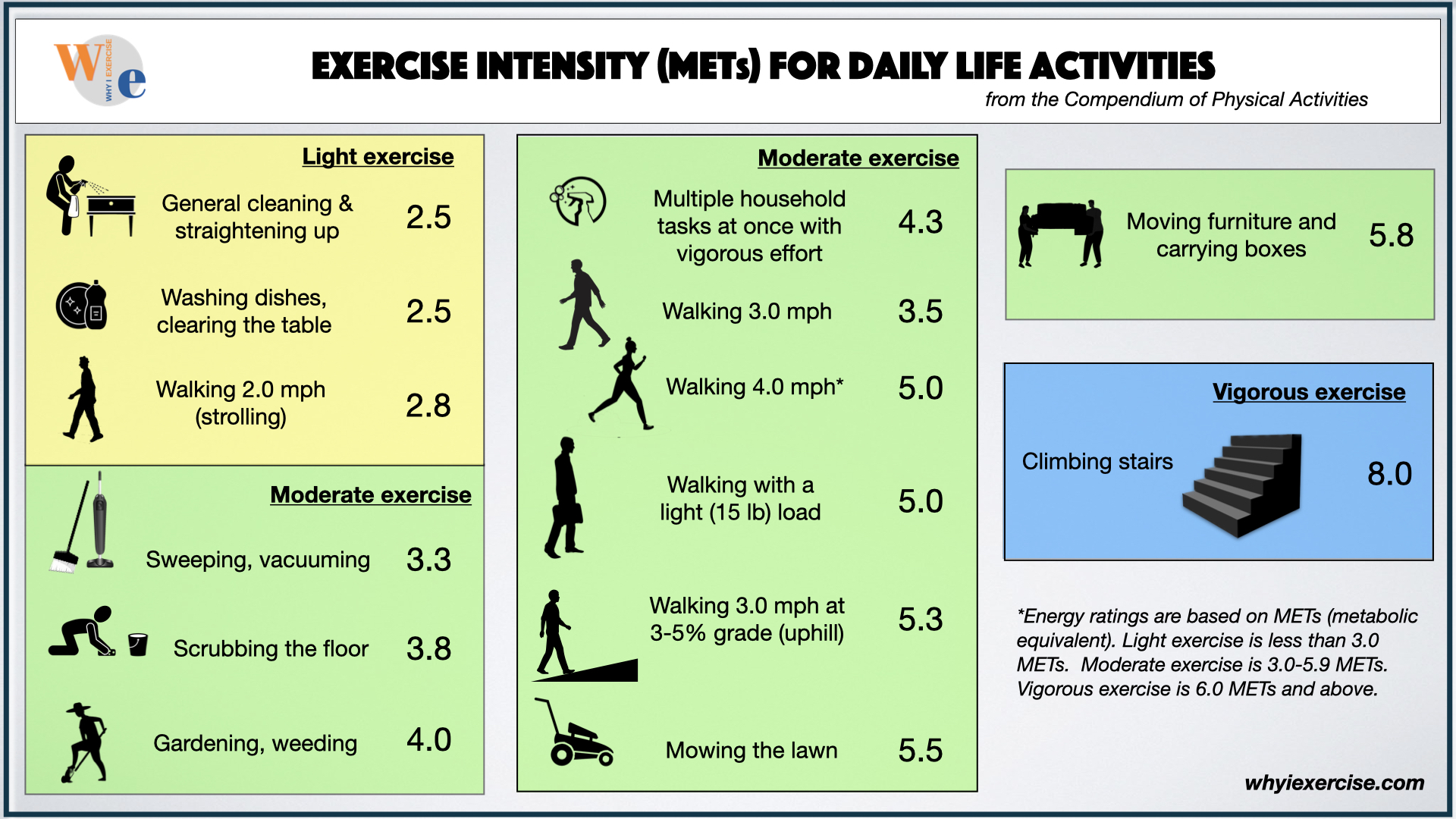
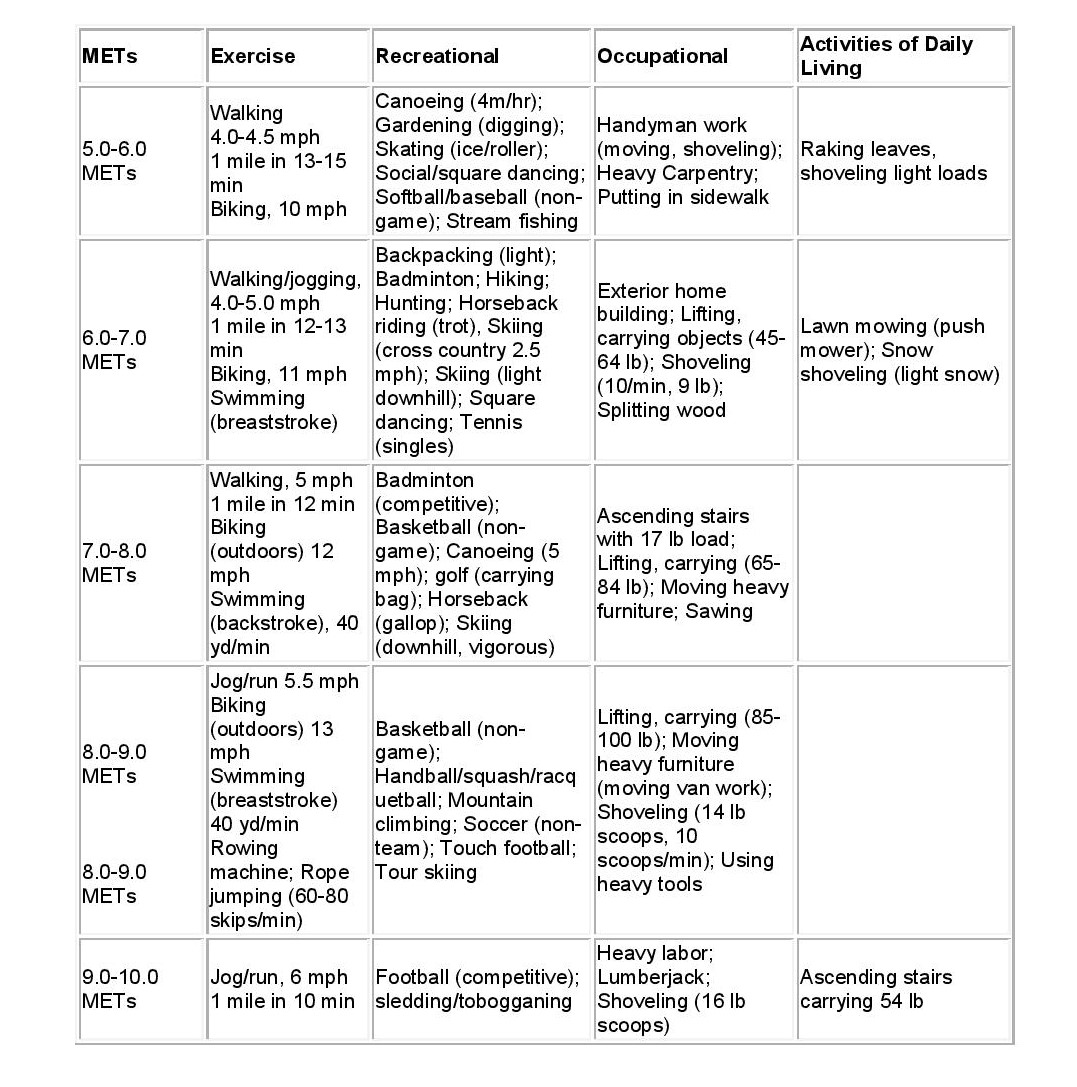
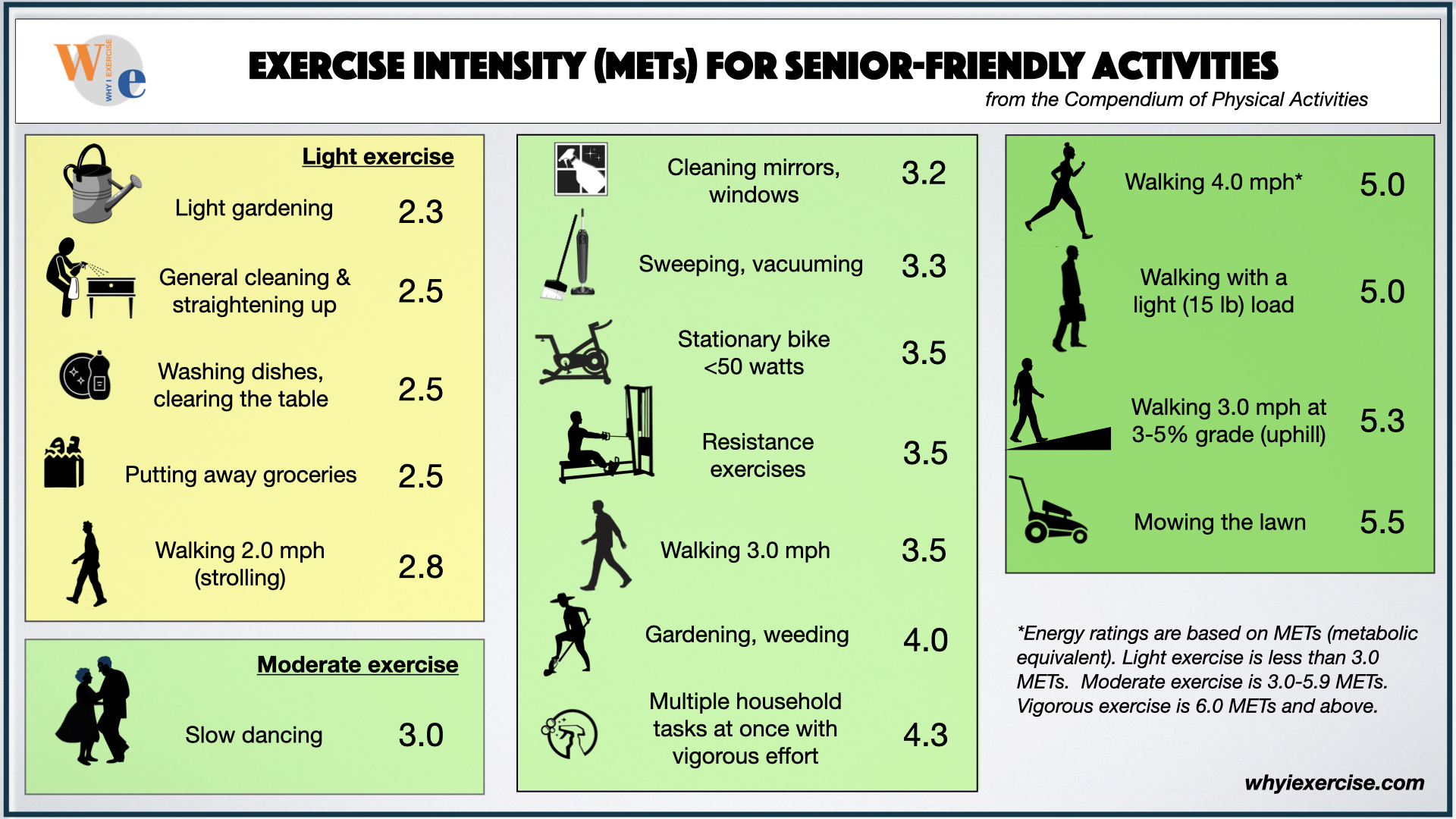
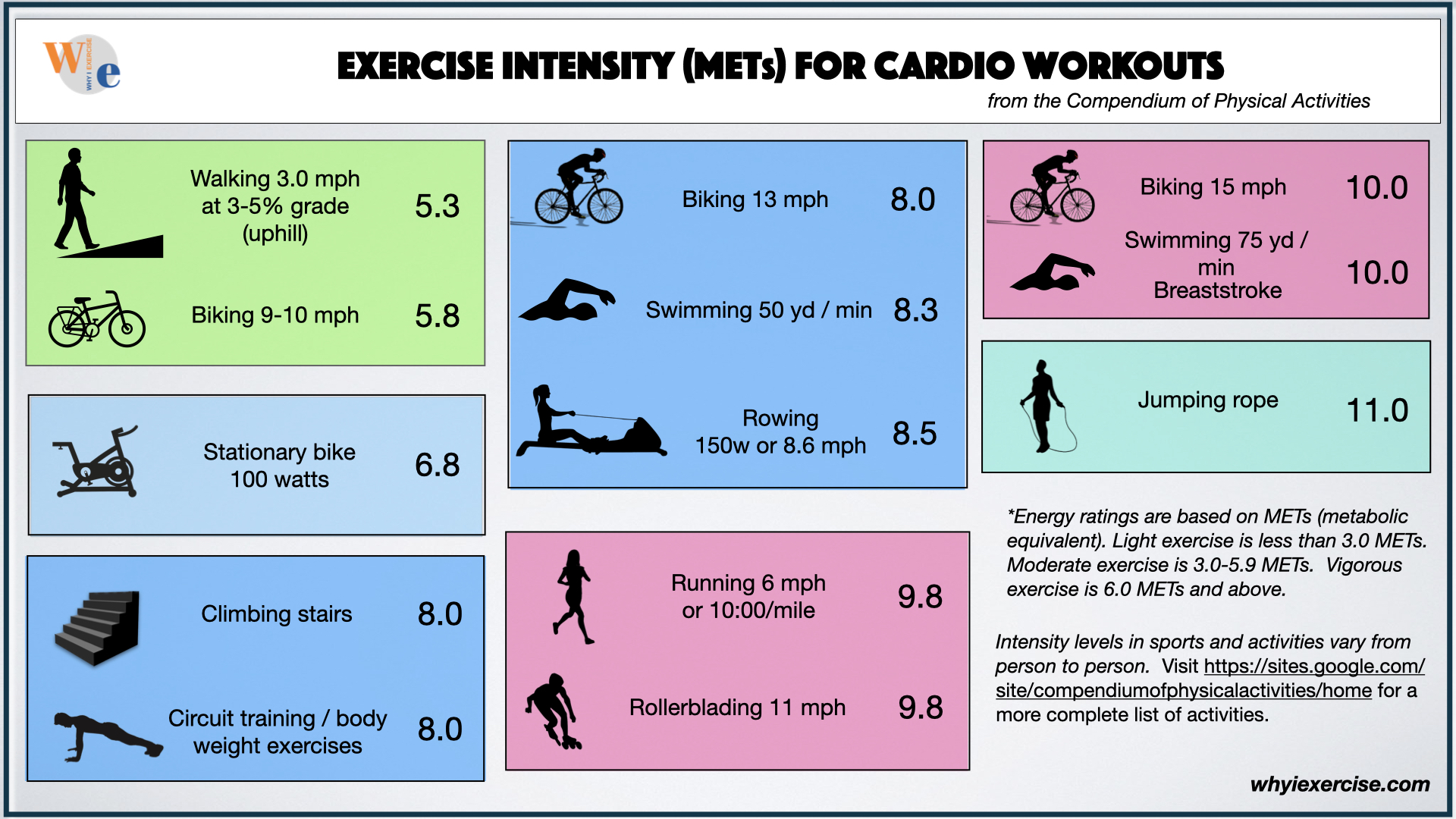
Mets are used to quantify The mets capacity is your upper limit of capacity to exercise and should not be confused with the recommended workout level. Web the chart below lists the number of mets used per hour during various types of physical activities. Web ask your client to pick a favorite physical activity or mode of exercise and plug the met value into the formula below to see how many calories they burn per minute and whether or not hey should increase the level of intensity or duration to help achieve a specific goal like weight loss: Web this chart provides approximate met values for a variety of light, moderate, and vigorous activities.
Thus, the maximum mets you can achieve and sustain for a few minutes tell about your exercise capacity. We will share several comprehensive met charts below as well. Mets x 3.5 x bw (kg) / 200 = kcal/min. Web metabolic equivalents, or mets, are an estimated measure of how much energy a given activity requires in the form of calories burned. Web for each person, the range for total daily energy expenditure is highly variable, it depends on many factors, including: A met score of 1 represents the amount of energy used when a person is at rest. When you are sitting on a chair, you are using 1 met. Try to increase your average met level during cardiac rehabilitation. Web compare mets (exercise intensity rating) for all kinds of exercise and activities in these charts. Web measuring metabolic energy equivalent (met) general information a metabolic energy equivalent (met) measures how much effort an activity requires from you. Gradually increase your resistance and speed to increase your met level. Activity level, age, gender, size, weight and body composition. Web met levels go over 10, but much of what you need to know for acute and inpatient rehab, e.g., for adls and iadls are covered up to 4.1 mets. Web ask your client to pick a favorite physical activity or mode of exercise and plug the met value into the formula below to see how many calories they burn per minute and whether or not hey should increase the level of intensity or duration to help achieve a specific goal like weight loss: Web the chart below lists the number of mets used per hour during various types of physical activities.
Web Met Chart Approximate Energy Cost Of Activities — 1 Met Is The Energy Expenditure At Rest Note:
Web a met, or metabolic equivalent, is described as the amount of energy it costs to complete a task, determined by the amount of oxygen it requires. A met also is defined as oxygen uptake in ml/kg/min with one met equal to the oxygen cost of sitting quietly, equivalent to 3.5 ml/kg/min. Web a met, or (metabolic equivalent), is described as the amount of energy it costs to complete a task, determined by the amount of oxygen it requires. 1 met is equal to 3.5ml/kg/min of o2.
An Update Of Activity Codes And Met Intensities.
Try to increase your average met level during cardiac rehabilitation. Gradually increase your resistance and speed to increase your met level. Web a quick summary to keep in mind: Web met levels go over 10, but much of what you need to know for acute and inpatient rehab, e.g., for adls and iadls are covered up to 4.1 mets.
L Light Activities (< 3 Mets) Are Good For Elderly Persons And Those Who May Have Physical Limitations, Or Someone Recovering From An Illness Who Needs To Gradually Increase Their Activity Level.
Web for each person, the range for total daily energy expenditure is highly variable, it depends on many factors, including: Web compare mets (exercise intensity rating) for all kinds of exercise and activities in these charts. Thus, the maximum mets you can achieve and sustain for a few minutes tell about your exercise capacity. 1 met is equal to 3.5ml/kg/min of o2.
Here's How To Use Them.
A met score of 1 represents the amount of energy used when a person is at rest. Web the chart below lists the number of mets used per hour during various types of physical activities. Web metabolic equivalents, or mets, are an estimated measure of how much energy a given activity requires in the form of calories burned. One met is defined as 1 kcal/kg/hour and is roughly equivalent to the energy cost of sitting quietly.