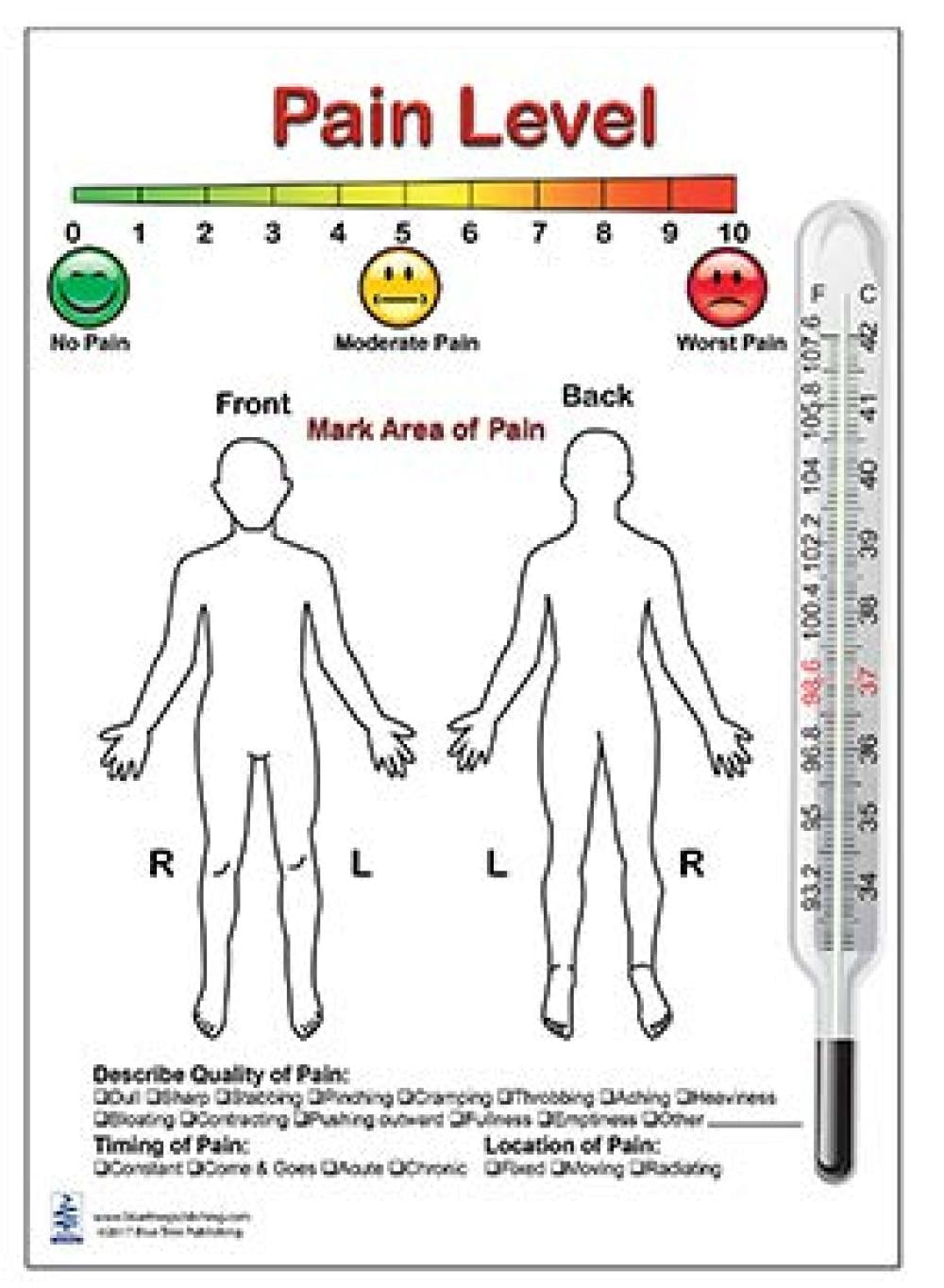
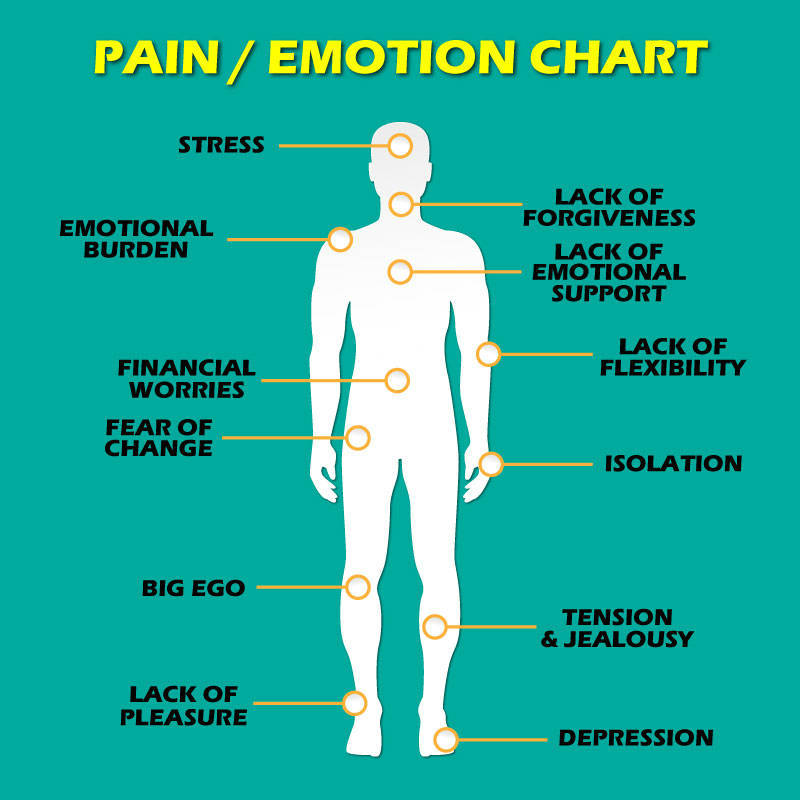
Pain is the most common reason for physician consultation in most developed countries. Pain management may include changing your position, using ice or heat, or taking medicine. Web to get good control of your chronic pain, it's not enough to tell your doctor it hurts. Move your mouse over the different body parts in order to read more of the different chronic painful conditions. See the different pain scales in use and how they work to qualify and quantify your pain.
Move your mouse over the different body parts in order to read more of the different chronic painful conditions. Such information can be used to diagnose painful conditions more reliably and to guide optimal treatment. You need to learn how to talk about pain: Web most pain scales use numbers from 0 to 10. How it feels, how it rates on a pain scale, and how it affects.
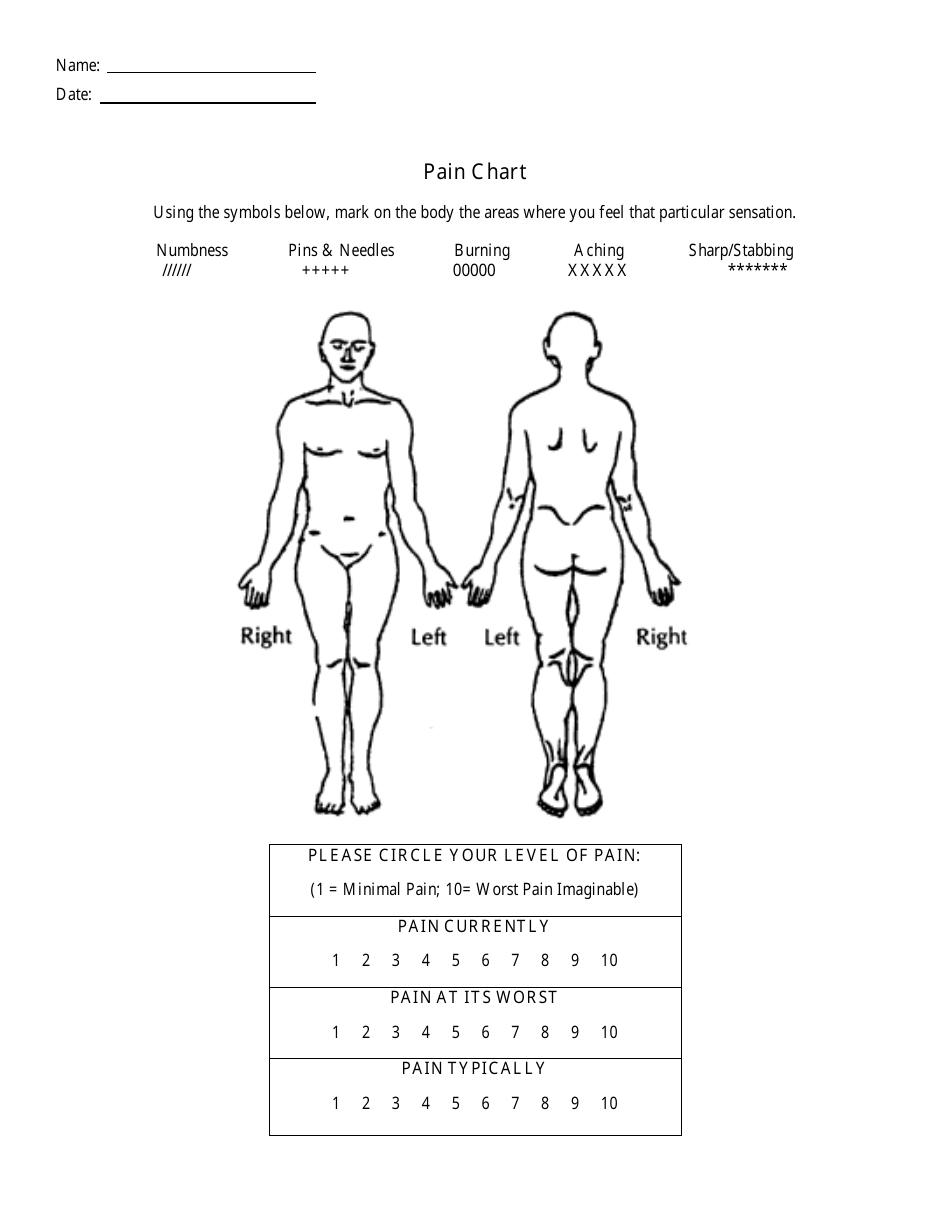
Completed charts assist in diagnosis and treatment planning, enabling personal pain tracking and discussion with healthcare teams. They may then combine this. Whether your pain is acute (sudden and severe) or chronic (persistent or recurrent), communicating your experience of pain can help your healthcare provider prescribe the best possible treatments for your type and level of pain. Web michigan body map on the image below, check all areas of your body where you have felt persistent or recurrent pain present for the last 3 months or longer (chronic pain). Web at this time, where is your pain?
They may then combine this. Web a pain scale chart can help people describe the pain they are feeling. What word best matches how it feels? Your medical team will help you manage your pain in a variety of ways. Web a pain chart is a detailed tool that depicts a human body or a scale medical professionals and patients may use to discover the location of pain and the intensity of this discomfort. Web body pain charts were introduced as part of the mcgill pain questionnaire. Web michigan body map on the image below, check all areas of your body where you have felt persistent or recurrent pain present for the last 3 months or longer (chronic pain). How it feels, how it rates on a pain scale, and how it affects. Completed charts assist in diagnosis and treatment planning, enabling personal pain tracking and discussion with healthcare teams. Web a pain diagram, also known as a body map, is simply a visual representation of the location and intensity (usually indicated by color) of one’s pain. Whether your pain is acute (sudden and severe) or chronic (persistent or recurrent), communicating your experience of pain can help your healthcare provider prescribe the best possible treatments for your type and level of pain. You need to learn how to talk about pain: Here are the different types, pros and cons, and a chart with faces. Whilst someone else will be overwhelmed form the pain from such an injury. Web most pain scales use numbers from 0 to 10.
Move Your Mouse Over The Different Body Parts In Order To Read More Of The Different Chronic Painful Conditions.
It is a significant symptom in many medical conditions and can interfere with a person's quality of life and general functioning. Web at this time, where is your pain? Whether your pain is acute (sudden and severe) or chronic (persistent or recurrent), communicating your experience of pain can help your healthcare provider prescribe the best possible treatments for your type and level of pain. Web a pain diagram, also known as a body map, is simply a visual representation of the location and intensity (usually indicated by color) of one’s pain.
Web By Using A Pain Chart Body Diagram, Patients Can Visually Communicate The Intensity And Location Of Their Pain, Allowing Healthcare Professionals To Select The Most Appropriate Interventions And Pain Management Strategies.
Pain is the most common reason for physician consultation in most developed countries. You need to learn how to talk about pain: Here are the different types, pros and cons, and a chart with faces. Acute pain usually comes on suddenly and lasts for a limited time.
It Helps To Provide Doctors With An Understanding Of The Location And Type Of Discomfort Experienced By Their Patients Which Makes It Easier For Them To Prescribe Necessary Treatments.
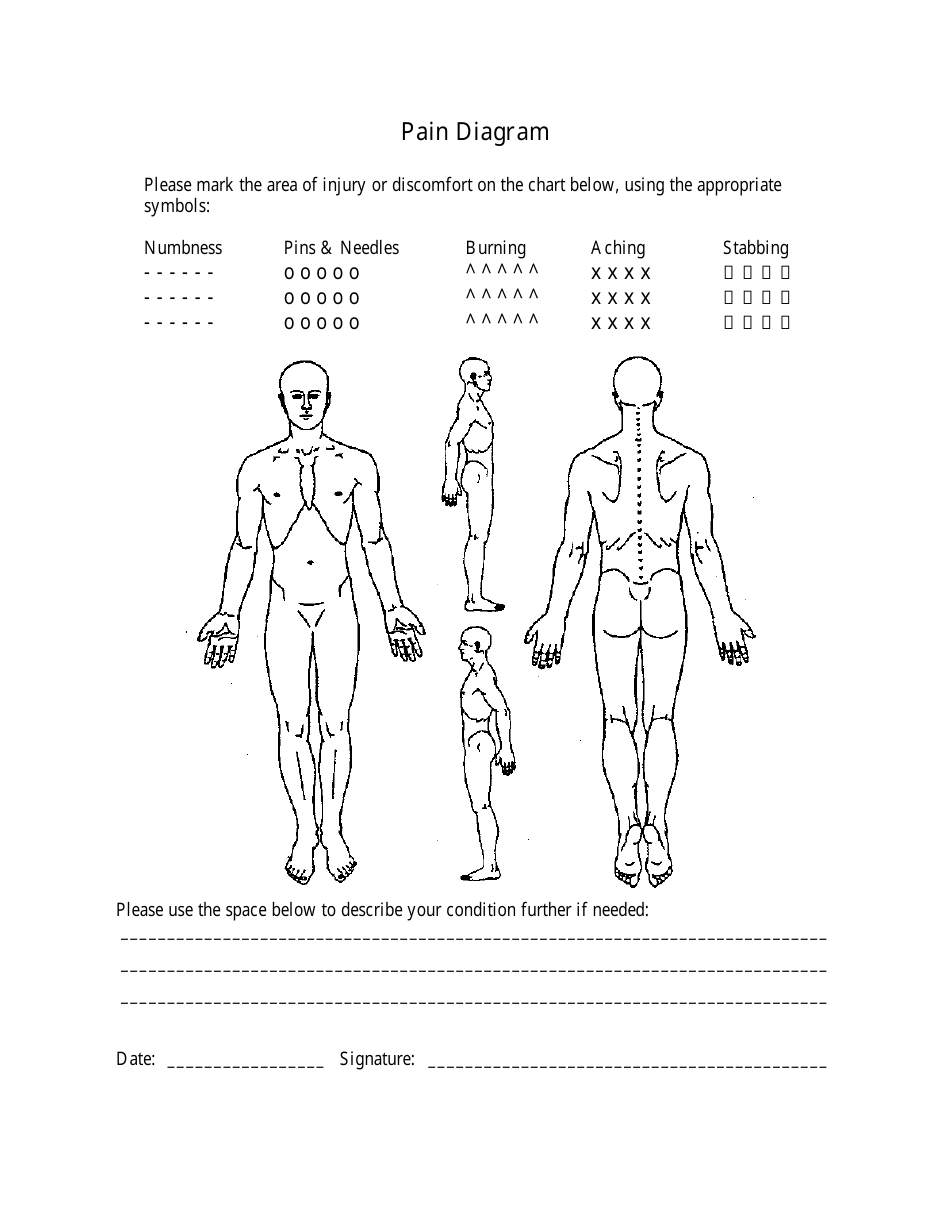
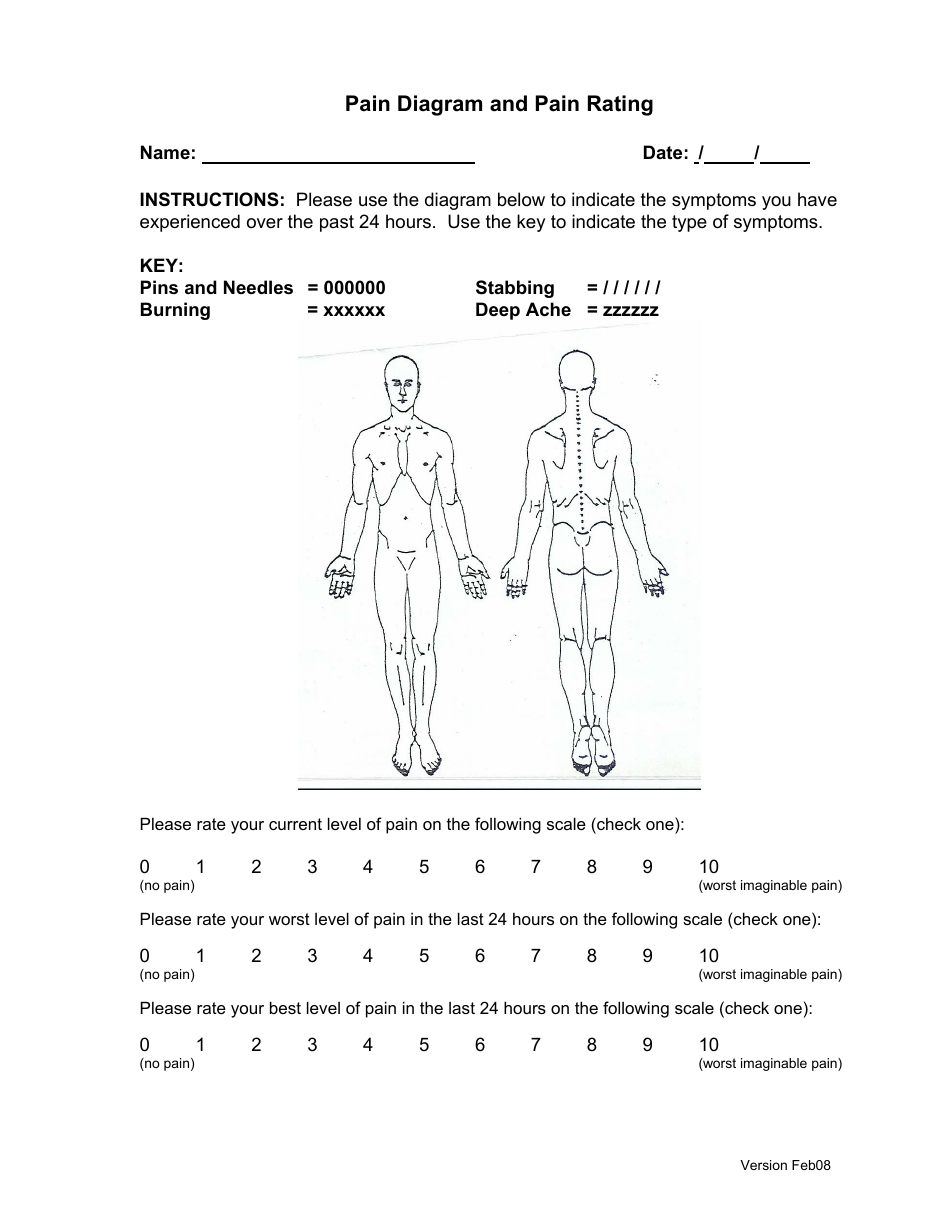
Please mark on the drawings the area where you feel pain (circle or mark with crosses) pain rating (on scale of 0 to 10, with 10 the worst) Do not indicate areas of pain which are not related to your present injury condition. Dicate where your pain is located and what type of pain you feel at the present time. Web body pain charts were introduced as part of the mcgill pain questionnaire.
How It Feels, How It Rates On A Pain Scale, And How It Affects.
Web people experience pain in different ways. Web most pain scales use numbers from 0 to 10. Web individuals mark pain areas on a body diagram to use them, describe sensations using a key, rate intensity, and specify details. Stinging, penetrating, dull, throbbing, achy, nagging, gnawing.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-539684888-5a90af7ec064710037753911.jpg)