Single and multiple covalent bonds. A shorter bond length has higher bond energy. Web the amount of energy required to break all covalent bonds of the same type in one mole of a compound in a gaseous state is called bond energy. As we go across a period we see bond length decreases. Before we go into the details explaining the bong lengths and bond strengths in organic chemistry, let’s put a small summary for these two properties right from the beginning as it stays relevant for all types of bonds we are going to talk about.
Web the amount of energy required to break all covalent bonds of the same type in one mole of a compound in a gaseous state is called bond energy. Before we go into the details explaining the bong lengths and bond strengths in organic chemistry, let’s put a small summary for these two properties right from the beginning as it stays relevant for all types of bonds we are going to talk about. Web below is a table of average bond lengths. Bond order is the number of electron pairs that hold two atoms together. Web from this graph, we can determine the equilibrium bond length (the internuclear distance at the potential energy minimum) and the bond energy (the energy required to separate the two atoms).
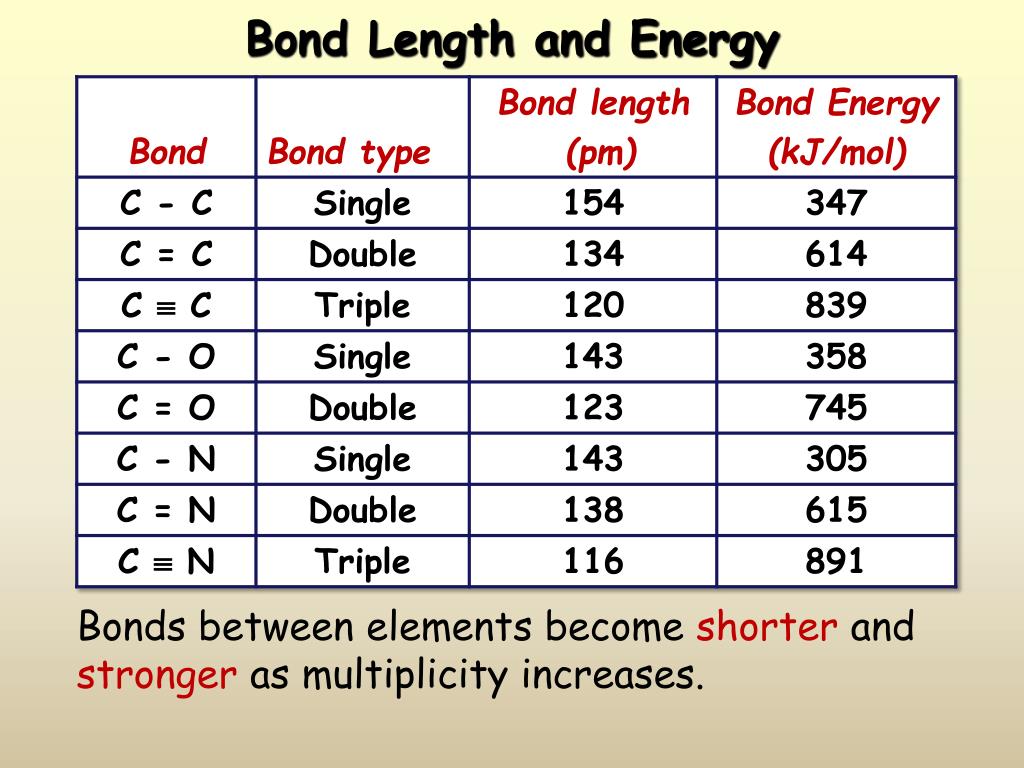
Web below is a table of average bond lengths. A shorter bond length has higher bond energy. Bond length and bond strength. The bond energy is inversely proportional to the bond length. Bond energies and bond lengths.
Web from this graph, we can determine the equilibrium bond length (the internuclear distance at the potential energy minimum) and the bond energy (the energy required to separate the two atoms). A shorter bond length has higher bond energy. It is a transferable property of a bond between atoms of fixed types, relatively independent of the rest of the molecule. 8.9.1), where the bottom of the well represents the equilibrium position of the oscillating atoms, which. A bond is not static but dynamic with the atoms undergoing the attractive and repulsive forces as described in the potential well (fig. Lewis diagram of formaldehyde (ch₂o) This is because as we go down the group, the atomic radius increases. As we go across a period we see bond length decreases. Bond length and bond strength. Predicting bond type (metals vs. Web the amount of energy required to break all covalent bonds of the same type in one mole of a compound in a gaseous state is called bond energy. Web in molecular geometry, bond length or bond distance is defined as the average distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. Web below is a table of average bond lengths. Bond order is the number of electron pairs that hold two atoms together. Before we go into the details explaining the bong lengths and bond strengths in organic chemistry, let’s put a small summary for these two properties right from the beginning as it stays relevant for all types of bonds we are going to talk about.
A Shorter Bond Length Has Higher Bond Energy.
Web bond length is defined as the distance between the centers of two covalently bonded atoms. Bond length and bond strength. As we go across a period we see bond length decreases. Browse videos, articles, and exercises by topic.
Bond Order Is The Number Of Electron Pairs That Hold Two Atoms Together.
Web from this graph, we can determine the equilibrium bond length (the internuclear distance at the potential energy minimum) and the bond energy (the energy required to separate the two atoms). A bond is not static but dynamic with the atoms undergoing the attractive and repulsive forces as described in the potential well (fig. Single bonds have a bond order of one, and multiple bonds with bond orders of two (a double bond) and three (a triple bond). The higher the bond order, the stronger the pull between the two atoms and the shorter the bond length.
Bond Energies And Bond Lengths.
Single and multiple covalent bonds. The bond energy is inversely proportional to the bond length. Lewis diagram of formaldehyde (ch₂o) 8.9.1), where the bottom of the well represents the equilibrium position of the oscillating atoms, which.
Web Below Is A Table Of Average Bond Lengths.
Web the amount of energy required to break all covalent bonds of the same type in one mole of a compound in a gaseous state is called bond energy. It is a transferable property of a bond between atoms of fixed types, relatively independent of the rest of the molecule. This unit is part of the chemistry library. The length of the bond is determined by the number of bonded electrons (the bond order).

![Bond lengths [Å] and angles [°] for 4c Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333256073/figure/download/tbl2/AS:761180935159811@1558491085331/Bond-lengths-A-and-angles-for-4c.png)





.PNG)
